7.4. SDM-LKM Equivalence#
7.4.1. Relation among DSM, LKM and EDM#
With regard to the relation to the stochastic models, there is a notable paper [FCD04] which suggests:
Note
This equivalence, in our application, is under investigation.
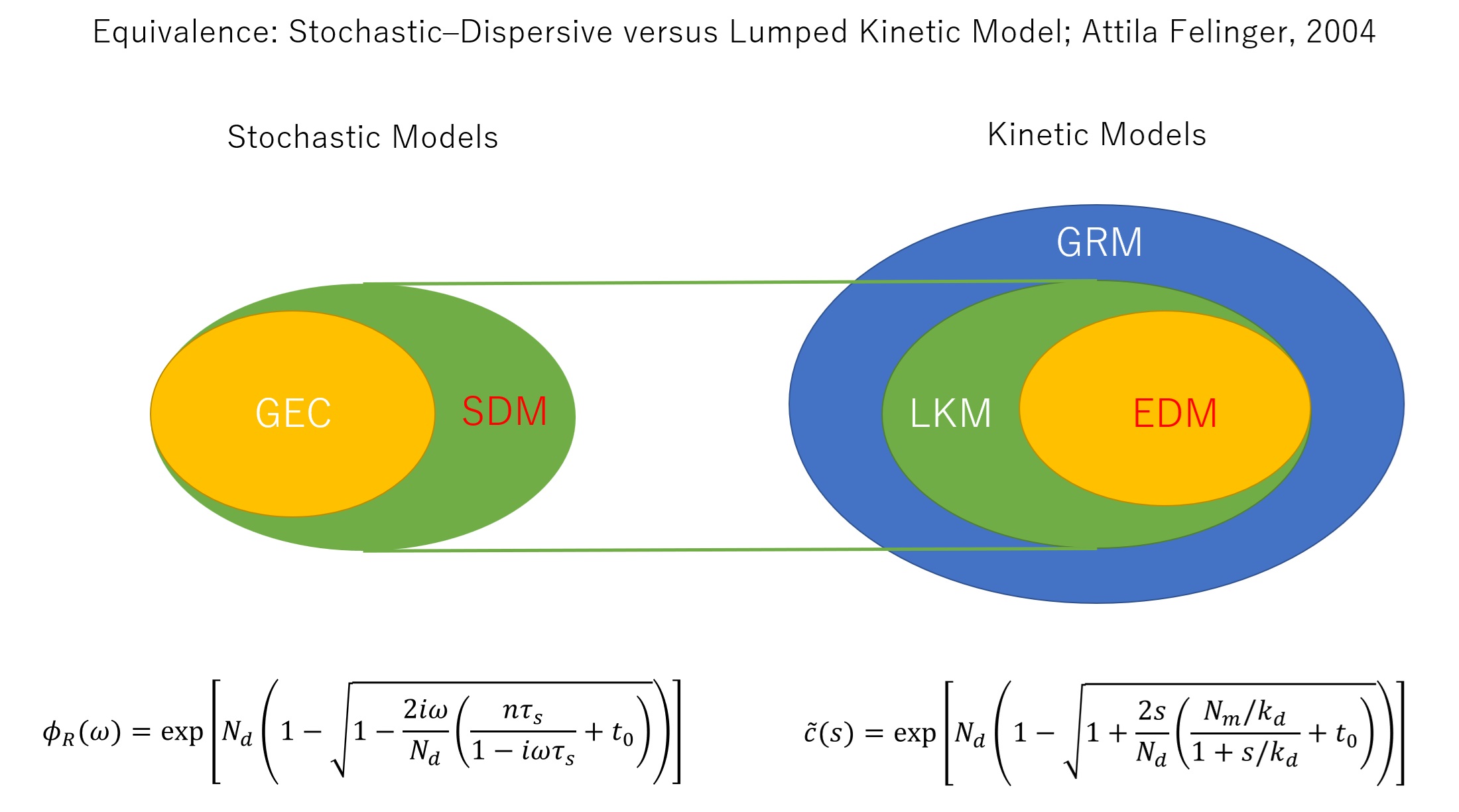
Fig. 7.2 SDM-LKM Equivalence#
7.4.2. Notational Correspondence in Relevant Papers#
Here are summarized notational correspondence among the relevant papers:
Dondi-2002 SDM |
Felinger-2004 LKM |
Rehman-2021 EDM |
Parameter Despription |
|---|---|---|---|
\( N_0 \) |
\( N_d = \frac{Lu}{2D} \) |
\( \frac{Lu}{2D_z} \) |
Number of Plates in Mobile Zone; \( N_0 = N_d = (\frac{t_0}{\sigma_0})^2 \) |
\( n_i \) |
\( N_m \) |
Average Number of Stays in Stagnant Zone; \(N_m=F k_a t_0 = k' k_d t_0 \); \( k' = \frac{F k_a}{k_d} \) |
|
\( \tau_i \) |
\(\frac{1}{k_d} \) |
Average Time of Stays in Stagnant Zone; \( \frac{1}{k_d} = \frac{k' t_0}{N_m} \) |
|
\( K_{SEC} \) |
\( e \) (porosity) |
\( e \) (porosity) |
\( \rho = \min(1, \frac{R_g}{R_p}) \) ; \( K_{SEC} = (1 - \rho)^m \) ; \( (K_{SEC})^{\frac{1}{m}} = 1 - \rho \) ; \( R_g \sim R_p(1 - porosity^{\frac{1}{m}}) \) |
7.4.3. SymPy Examples to Understand the Papers#
To follow the papers, you can use SymPy. Here are some examples.
from sympy import symbols, Eq, Function, dsolve
f, g = symbols("f g", cls=Function)
x = symbols("x")
eqs = [Eq(f(x).diff(x), g(x)), Eq(g(x).diff(x), f(x))]
dsolve(eqs, [f(x), g(x)])
[Eq(f(x), -C1*exp(-x) + C2*exp(x)), Eq(g(x), C1*exp(-x) + C2*exp(x))]
dsolve(eqs, [f(x), g(x)], ics={f(0): 1, g(2): 3})
[Eq(f(x), (1 + 3*exp(2))*exp(x)/(1 + exp(4)) - (-exp(4) + 3*exp(2))*exp(-x)/(1 + exp(4))),
Eq(g(x), (1 + 3*exp(2))*exp(x)/(1 + exp(4)) + (-exp(4) + 3*exp(2))*exp(-x)/(1 + exp(4)))]
eqn = Eq(f(x).diff(x), f(x))
dsolve(eqn, f(x), ics={f(x).diff(x).subs(x, 1): 2})
from sympy import symbols, Function, dsolve
t = symbols('t')
y = Function('y')(t)
y
yp = y.diff(t)
ypp = yp.diff(t)
eq = ypp + 2*yp + y
eq
dsolve(eq, y)
dsolve(eq, y, ics={y.subs(t, 0): 0})
